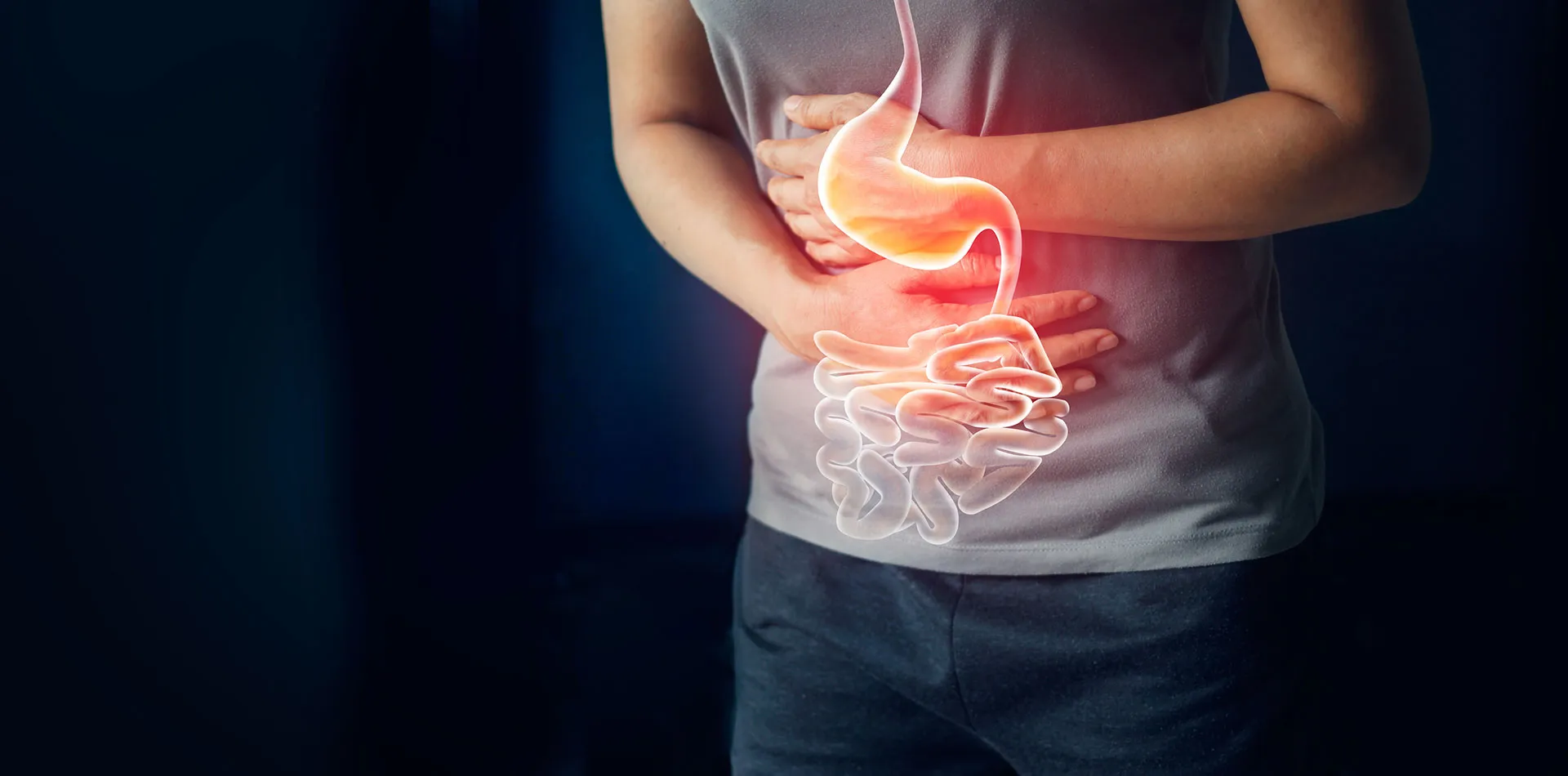
Indigestion, known as dyspepsia, is a condition that upsets the stomach causing discomfort in the upper abdomen. The main signs of indigestion are abdominal pain and a feeling of fullness after you start to eat, and it may indicate various types of digestive diseases.
Experiencing indigestion is a common state, but the feeling may slightly differ with each person. People may feel the symptoms occasionally or as often, even daily, but the impact can be lessened and relieved with lifestyle changes and medications.
The most common signs of indigestion are:
• You feel full during a meal soon after starting to eat, even when you have not eaten much.
• After the meal, an uncomfortable feeling of fullness lasts for long hours.
• You may have discomfort in the upper abdomen, like mild to severe pain between the bottom of your breastbone and belly button.
• You experience a feeling of uncomfortable heat or burning sensation between the bottom of your breastbone and belly button.
• You are bloating, an uncomfortable sensation of tightness in the upper abdomen.
• You have a sensation to vomit and belch, but it is a less common sign.
• In some rare cases, people may have heartburn - pain or burning feeling in the center of the chest, spreading to the neck or back during or after eating.
Mild indigestion must not be a cause of concern, but when the discomfort lasts for over two weeks, get the doctor's advice.
Contact your doctor immediately when you have severe pain and experience repeated vomiting or vomiting with blood or unintentional weight loss or loss of appetite.
Also, get medical help when you have black, tarry stools, trouble swallowing that is gradually worsening, or feel tired or weak, indicating anemia.
Ask for prompt medical attention when you have shortness of breath, sweating, or chest pain radiating to the jaw, neck or arm, or chest pain on exertion or with stress.
Multiple reasons may lead to an indigestion state, like lifestyle conditions or food, drink or medication that trigger the digestion issue.
The common reasons for indigestion are overeating or eating too fast, having fatty, greasy or spicy foods, too much caffeine, alcohol, chocolate or carbonated beverages. Smokers, people with anxiety and those using some antibiotics, pain relievers and iron supplements can trigger the condition.
An indigestion state is referred to as functional or non-ulcer dyspepsia linked to irritable bowel syndrome, a prevalent cause of the illness.
The other conditions include inflammation of the stomach (gastritis), pancreas inflammation (pancreatitis), celiac disease, gallstones, peptic ulcers and constipation. A stomach cancer, intestinal blockage, diabetes, thyroid disease, pregnancy or reduced blood flow in the intestine (intestinal ischemia) are cause indigestion problems.
Indigestion is usually not a severe complication but impacts the quality of life as the person may feel uncomfortable and eat less. Also, this condition can lead to missing work or school because of your symptoms.
Specific lifestyle changes and care can improve digestion and relieve uncomfortable symptoms:
• Eat smaller portions of meals.
• Skip spicy, fatty foods that cause heartburn.
• Eat slowly, sitting straight and never lying down.
• Quit smoking.
• Reduce your excess body weight.
• Limit consumption of coffee, soft drinks, and alcohol you take.
• Take plenty of rest, and lessen all stressors.
• Consult the doctor to know the medications that can irritate the stomach lining, and seek their advice.
Patient Experience