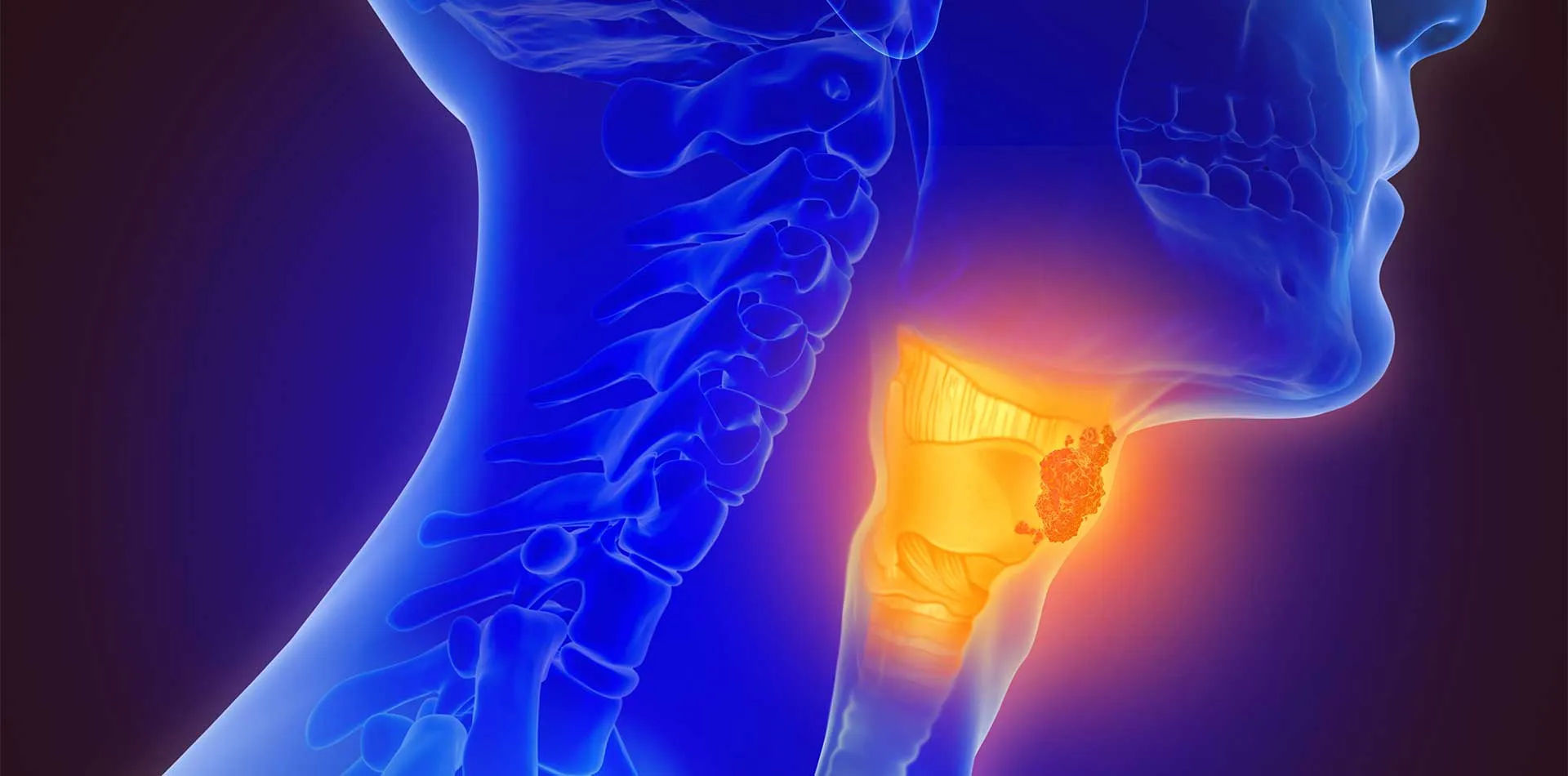
Throat cancer happens in the voice box or throat - a muscular tube that begins behind the nose and ends in the neck. Throat cancer, also called pharyngeal cancer, develops in the flat cells that outline the inside of the throat. The voice box sits below the throat and contains vocal cords that vibrate to create sounds when talking, developing laryngeal cancer.
The type of throat cancer differentiates based on the part where it originates.
• Nasopharyngeal cancer happens in the part of the throat that is behind the nose.
• Oropharyngeal cancer occurs in the throat right behind the mouth that has tonsils.
• Hypopharyngeal cancer occurs in the lower part of the throat, above the esophagus and windpipe.
• Glottic cancer appears in the vocal cords.
• Supraglottic cancer occurs in the upper portion of the voice box.
• Subglottic cancer arises in the lower part of the voice box below the vocal cords.
Signs of throat cancer are weight loss, cough, sore throat, ear pain, difficulty in swallowing, lump or sore that doesn't heal and changes in the voice, like hoarseness or not speaking clearly.
Talk to your doctor when you have some new signs that last for long. The symptoms are usually not specific to cancer; the doctor can diagnose the condition.
Throat cancer happens when cells in the throat develop genetic mutations that cause cells to multiply uncontrollably and continue living even after the healthy cells die. The accumulating cells form a tumor in the throat, though the reason for this condition is not known.
The reasons for the rise in the risk of throat cancer are:
• Tobacco use, that is, smoking and chewing tobacco
• Drinking excessive alcohol
• Some viral infections, like human papillomavirus (HPV) and Epstein-Barr virus
• A diet requiring fruits and vegetables
• Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
• Exposure to toxic things at work
You can limit the risk of throat cancer by:
• Quit smoking and get some help to learn stop-smoking strategies, like medication, nicotine replacement products, and counselling.
• Limit alcohol drinking to moderation, which means only one drink a day for women and two drinks a day for men.
• Choose a healthy diet with various fruits and vegetables as vitamins and antioxidants can reduce the risk of throat cancer.
• Reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infection human papillomavirus (HPV) by limiting your number of sexual partners and use of condoms during sex. Even the
HPV vaccine is helpful to reduce the risk of throat cancer and other HPV-related cancers.
Patient Experience