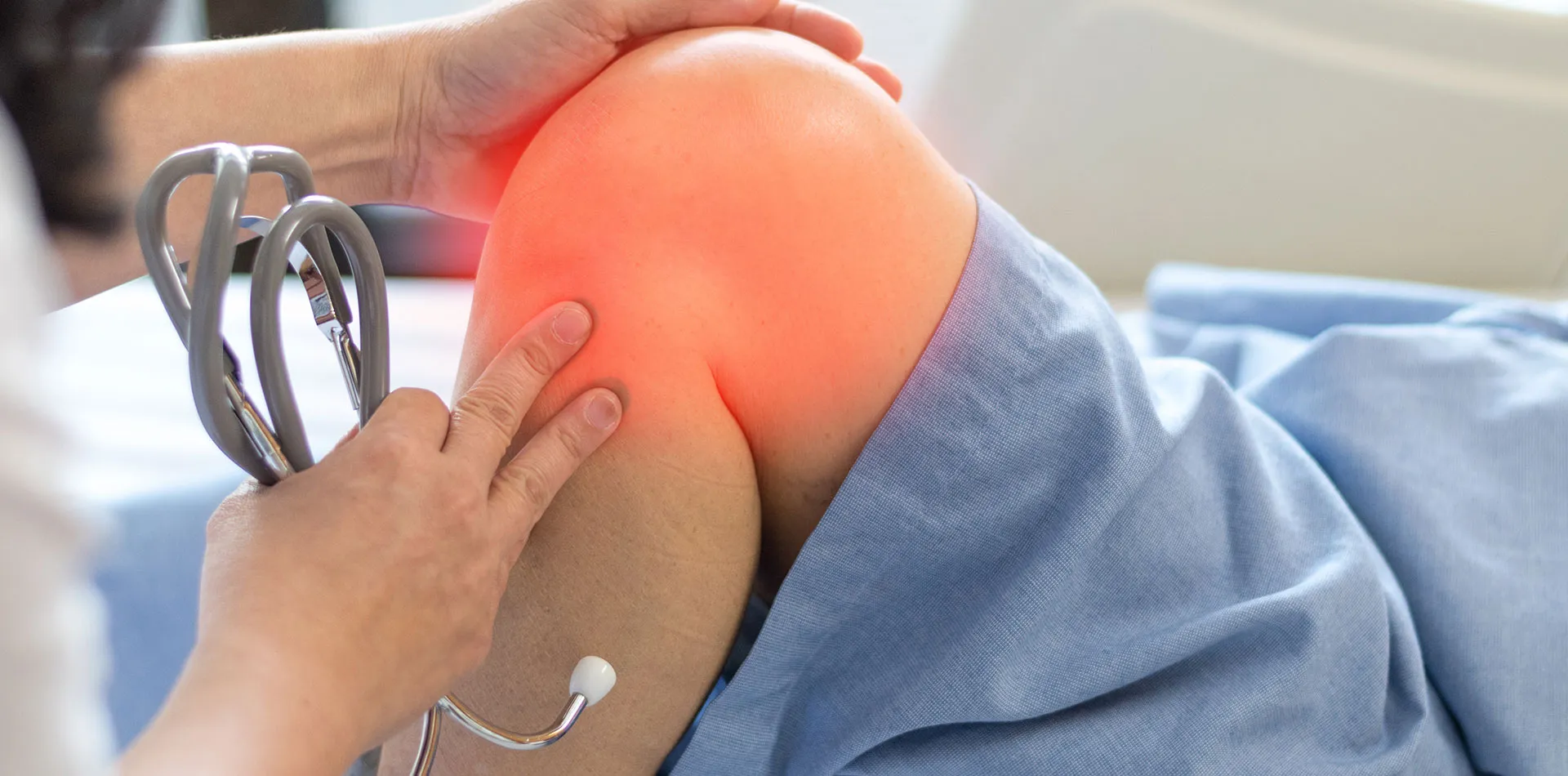
Osteochondritis dissecans is a painful joint problem in children and adolescents that most often occurs in the knee. In this condition, a lack of blood flow to the joint makes the bone soften, resulting in the bone and cartilage breaking loose, causing pain and probably limiting the joint motion. The other joints, such as elbows and ankles, may also get affected by this condition.
This type of condition may happen either after an injury to a joint or after several months of high-impact activity like jumping and running. Whether wholly or partially detached or still in its place, the size of the damage or crack will determine the severity of the patient's condition and symptoms.
When a loosened piece of cartilage and bone is in its place, there will be very few or no symptoms. Since young children bones are developing, they will heal by themselves; however, if the fragment is loosened and caught between the joint and the moving parts, and persistent pain occurs, surgery may become necessary.
• Based on the joint that's damaged, the person with osteochondritis dissecans may experience the following symptoms:
• Pain: Any physical activity that involves joint movement like walking upstairs, climbing a hill or playing sports can trigger the pain.
• Swelling and tenderness: You might see the skin around the joint as swollen and tender.
• Joint popping or locking: When a loose fragment is caught between bones during movement, the joint might get stuck in one position.
• Joint weakness: You may experience that the joint is weakening or giving way.
• Reduced range of motion: The movement of the affected limb may become restricted; that is, you are unable to straighten it completely.
When there is constant pain or soreness in the affected joint - knee, elbow or another joint, you must visit the doctor. Also, when you observe joint swelling or cannot move a joint through its full range of motion, you must seek advice from your physician.
Why osteochondritis dissecans happens remains unknown, but the decreased blood supply to the end of the affected bone occurs due to repetitive trauma. This may include small, multiple episodes of minor, unrecognized injury that is weakening the bone. Even genetic factors can lead to the development of such a disorder.
Osteochondritis dissecans disorder mainly affects children and adolescents aged 10 to 20, who are highly active in sports.
Osteochondritis dissecans might raise your chances of our risk of developing osteoarthritis in that joint.
Adolescents who are highly active in sports must be provided proper know-how on the risks of overusing their joints and must learn the correct mechanics and techniques of the game. Wearing the right protective gear is also essential, and strength training and stability training exercises further help reduce the chance of injury.
Patient Experience